FUEL SYSTEM
TESTING AND ADJUSTING
TM 5-3805-263-14&P-2
FUEL SYSTEM
Either too much fuel or not enough fuel for com-
bustion can be the cause of a problem in the fuel
system.
Many times work is done on the fuel system when
the problem is really with some other part of the
engine. The source of the problem is difficult to find,
especially when smoke comes from the exhaust.
Smoke that comes from the exhaust can be caused by
a bad fuel injection valve, but it can also be caused by
one or more of the reasons that follow:
a. Not enough air for good combustion.
b. An overload at high altitude.
c. Oil leakage into combustion chamber.
d. Not enough compression.
e. Fuel injection timing retarded.
FUEL SYSTEM INSPECTION
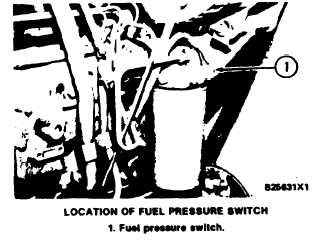
To check for low fuel pressure, remove fuel pres-
sure switch (1). Connect the 8M2743 Gauge from
the 5P6225 Hydraulic Test Box to the hole where
fuel pressure switch (1) was removed. Run the en-
gine at high idle and check the fuel pressure reading.
The fuel pressure must be at least 105 kPa (15 psi).
A problem with the components that send fuel to
the engine can cause low fuel pressure. This can
decrease engine performance.
1.
2.
Check the fuel level in the fuel tank. Look at the
cap for the fuel tank to make sure the vent is not
filled with dirt.
Check the fuel lines for fuel leakage. Be sure the
3.
4.
fuel supply line does not have a restriction or a
bad bend.
install a new fuel filter. Clean the primary fuel
filter.
Remove any air that may be in the fuel system. If
there is air in the fuel system, use the priming
pump and open the drain valve on the fuel injec-
tion pump housing until fuel without air comes
from the drain line.
CAUTION
When fuel injection lines are loosened or tight-
ened on the fuel injection nozzles, two
wrenches must be used. The nozzle must be
held with a wrench or damage to the nozzle can
result.
To remove air from the fuel injection lines, loosen
the fuel line nuts on the fuel injection nozzles 1/2
turn. Move the governor lever to the low idle position.
Crank engine with the starter motor until fuel with-
out air comes from the fuel line connections. Tighten
the fuel line nuts.
NOTE: The fuel priming pump will not give enough
pressure to push fuel through the reverse flow check
valves in the fuel injection pumps.
CHECKING ENGINE CYLINDERS
SEPARATELY
An easy check can be made to find the cylinder
that runs rough (misfires) and causes black smoke to
come out of the exhaust pipe.
Run the engine at the speed that is the roughest.
Loosen the fuel line nut at a fuel injection pump. This
will stop the flow of fuel to that cylinder. Do this for
each cylinder until a loosened fuel line is found that
makes no difference in engine performance. Be sure
to tighten each fuel line nut after the test before the
next fuel line nut is loosened. Check each cylinder by
this method. When a cylinder is found where the
loosened fuel line nut does not make a difference in
engine performance, test the injection pump and fuel
injection nozzle for that cylinder.
Temperature of an exhaust manifold port, when a
engine runs at low idle speed, can also be an indica-
tion of the condition of a fuel injection nozzle. Low
1-37