COOLING SYSTEM
TESTING AND ADJUSTING
TM 5-3805-263-14&P-2
C O O L I N G S Y S T E M
The engine has a pressure type cooling system. A
pressure type cooling system gives two advantages.
The first advantage is that the cooling system can
operate safely at a temperature that is higher than
the normal point where water changes to steam. The
second advantage is that this type system prevents
cavitation (air in inlet of pump) in the water pump.
With this type system it is more difficult for an air or
steam pocket to form in the cooling system.
The cause for an engine getting too hot is generally
because regular inspections of the cooling system
were not done. Make a visual inspection of the cool-
ing system before testing with testing equipment.
VISUAL INSPECTION OF THE COOLING
SYSTEM
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Check coolant level in the cooling system.
Look for leaks in the system.
Look for bent radiator fins. Be sure that air flow
through the radiator does not have a restriction.
Inspect the drive for the fan.
Check for damage to the fan blades.
Look for air or combustion gas in the cooling
system.
Inspect the pressure cap and the sealing surface
for the cap. The sealing surface must be clean.
Look for large amounts of dirt in the radiator
core and on the engine.
TESTING THE COOLING SYSTEM
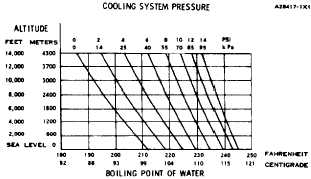
Remember that temperature and pressure work
together. When making a diagnosis of a cooling
system problem, temperature and pressure must
both be checked. Cooling system pressure will have
point (steam) of water.
an effect on cooling system temperatures. For an
example, look at the chart to see the effect of pres-
sure and the height above sea level on the boiling
Checking Coolant Temperatures
Tools Needed: 9S9102 Thermistor Thermometer Group.
The 9S9102 Thermistor Thermometer Group is
used in the diagnosis of overheating (engine running
too hot) or overcooling (engine running too cool)
problems. This group can be used to check the differ-
ent parts of the cooling system.
1-64