TM -3805-263-14&P-3
Fuel Specification
Diesel engines have the ability to burn a wide variety of
Coolant Specifications
fuels. These fuels are divided into two general groups,
Use a mixture of fill water, antifreeze and cooling system
preferred and permissible.
conditioner.
Types of Fuel
Fill Water
The preferred fuels provide maximum engine service life
Always add conditioner to water. Never use plain water
and performance. They are distillate fuels. They are
only.
commonly called fuel oil, furnace oil, diesel fuel, gas oil,
or kerosene.
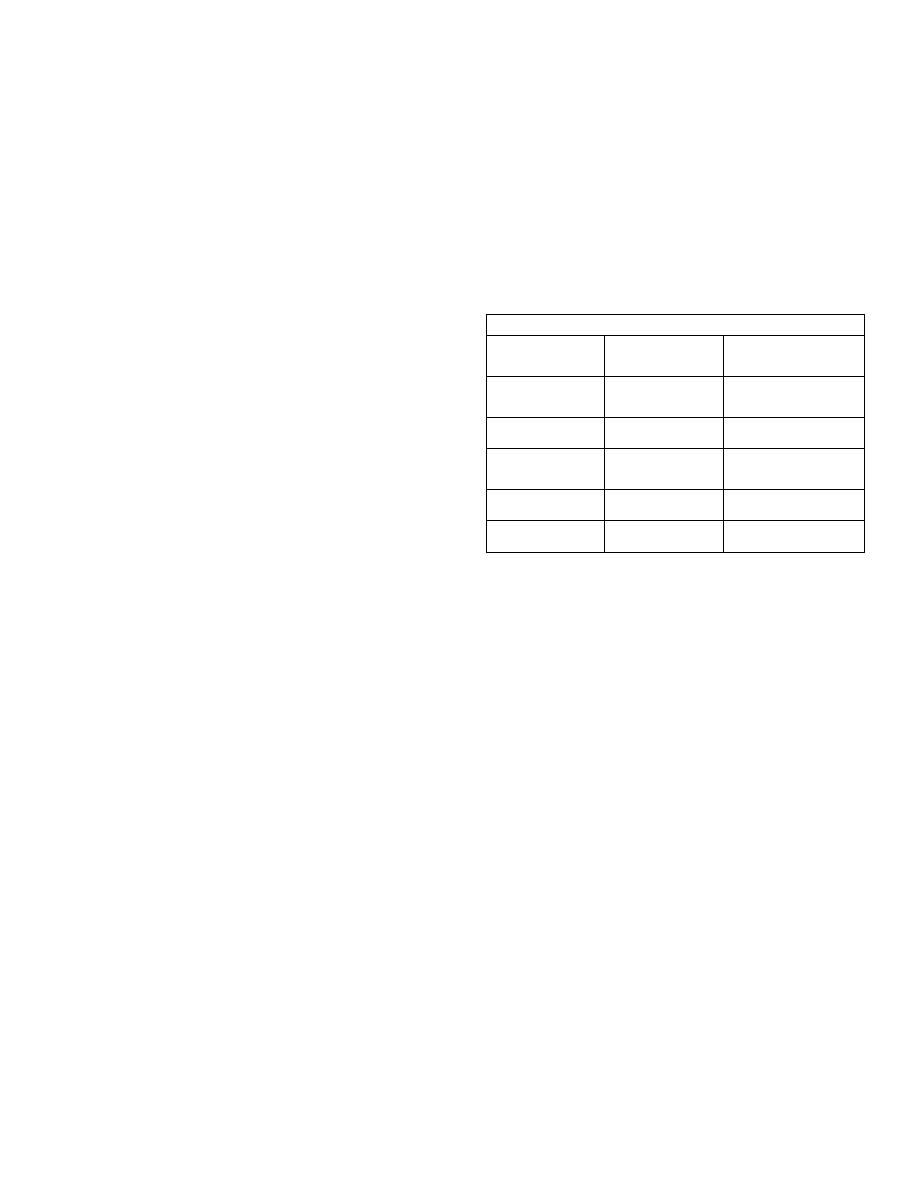
Acceptable water for use in the ethylene glycol-type
antifreeze and water mixture is shown on the chart
The permissible fuels are crude oils or blended fuels.
below:
Use of these fuels can result in higher maintenance
costs and reduced engine service life.
Acceptable Water
50%or More
Less Than
Water Content
Antifreeze
50% Antifreeze
Cetane Requirement
The minimum cetane number recommended for the
100 ppm
50 ppm
engine is 40.
or less
or less
Sulfates
100 ppm
50 ppm
Fuel Cloud Point
or less
or less
Fuel waxing can plug the fuel filters in cold weather. The
Hardness as
200 ppm
100 ppm
fuel cloud point must be below the temperature of the
CaCo3
or less
or less
surrounding air to prevent filter waxing and power loss.
Dissolved Solids
500 ppm
250 ppm
or less
or less
Fuel Sulfur Content
pH
6.5 or higher
6.5 or higher
The percentage of sulfur in the fuel will affect the engine
oil recommendations. If the fuel has over 0.5% sulfur
ppm = parts per million
content, the CD engine oil must have a TBN of 20 times
the percentage of fuel sulfur (TBN as measured by the
Antifreeze
ASTM D-2896 method).
Use ethylene glycol-type antifreeze. Use the correct
amount to provide freeze protection to the lowest
expected outside temperature.
Conditioner
Use cooling system conditioner to provide a 3% to 6%
concentration in the coolant. Follow the instructions on
the container.
3% = approximately 1 liter per 33 liters (1 pint per 4 U.S.
gal.)
6% = approximately 1 liter per 16 liters (1 pint per 2 U.S.
gal.)
5-10


