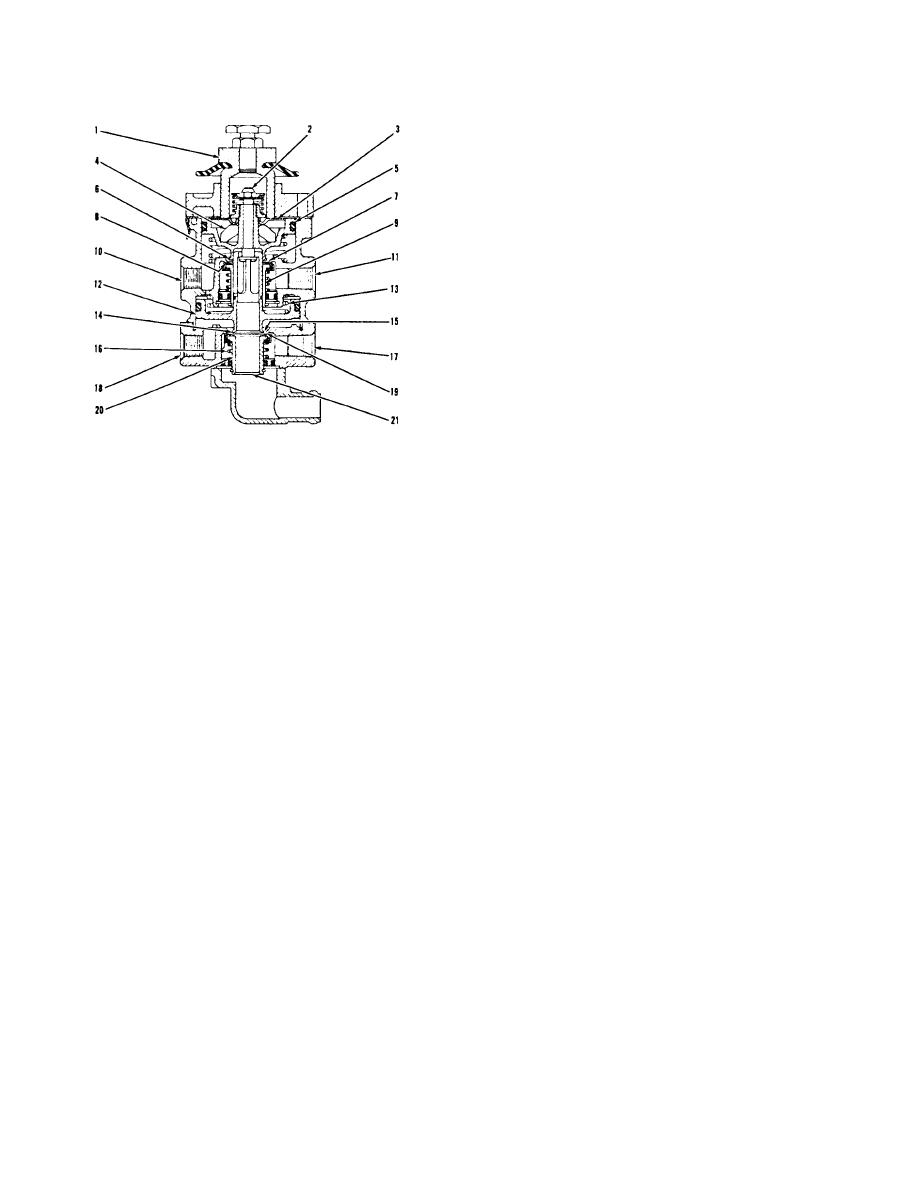
TM 5-3805-263-14&P-3
Brakes Balanced (Left Side)
When the air pressure under relay piston (12) is near the
air pressure on top of it, the relay piston (12) moves to
close the passage (15) and stops the flow of air from
supply port (17) to delivery port (18). Exhaust port (21)
will stay closed as the air pressure for the brakes on the
left side of the machine becomes the same as the air
pressure for the brakes on the right side of the machine.
When brake applications are made gradual, a
balance position in the section for the brakes on the right
side of the machine is reached when the air pressure at
the delivery port (10) is the same as the pressure of the
operator's foot on the pedal. A balance position is
reached in the section for the brakes on the left side of
the machine when the air pressure under the relay piston
(12) gets close (approaches) the air pressure above the
relay piston (12).
When the brake pedal is pushed all the way down,
both the inlet and exhaust valves (9) and (20) are open
CONTROL VALVE FOR SERVICE BRAKES
and full air pressure for the air tanks go to the brakes for
1.
Plunger.
2.
Screw.
3.
Spring seat.
4.
both sides of the machine.
Rubberspring. 5. Piston. 6. Seat. 7. Exhaust passage.
8. Seat. 9. Inlet and exhaust valve. 10. Delivery port.
SERVICE BRAKES
11. Supply port. 12. Relay piston. 13. Spring. 14.
The power from the differential is through drive chain (3)
Exhaust seat. 15. Exhaust passage. 16. Spring. 17.
to sprocket (1). The sprocket turns wheel spindle (5),
Supply port. 18. Delivery port. 19. Seat. 20. Inlet and
hub (2) and discs (8) in wheel spindle housing (13). The
exhaustvalve. 21. Exhaust port.
drive wheels are connected to flange (14) of wheel
spindle (5).
Loss of Brakes for Right Side
The disc-type brakes, one in each wheel spindle
Should air pressure in the circuit for the brakes on the
housing, are operated by air pressure from the relay
right side of the machine be lost, the brakes for the left
valves. Each brake is made up of discs (7) connected to
side of the machine can still be applied. As the brake
spindle housing (13) and discs (8) connected to hub (2).
pedal is pushed, and there is no air pressure at supply
The cooling of the brakes is through the oil in the drive
port (11) and delivery port (10), there will be no brakes
tandems.
for the right side of the machine. Piston (5) will
When the control valve opens, pressure air goes
mechanically move relay piston (12) to close inlet and
through port (10) into air compartment (9). Air then
exhaust valve(20) and let air pressure from supply port
moves piston (11) against discs (7) and (8). The piston
(17) go out delivery port (18) to the brakes for the left
pushes the discs against cover (6). As the air pressure
side of the machine.
becomes higher, the force of piston (11) pushing against
the discs causes friction between the discs. As the
Brakes Balanced (Right Side)
friction becomes greater, discs (8), hub (2), and wheel
When the air pressure at the delivery port (10) is the
spindle (5) will start to slow down, since discs (7) and
same as the mechanical force of the brake pedal, piston
wheel spindle housing (13) cannot turn. This is the
(5) will move and the inlet and exhaust valve (9) will
brake ON position, but the brakes are not fully engaged.
close and stop the flow of air from supply port (11). The
inlet and exhaust valve (20) will stay closed and will not
let air pressure go out through exhaust port (21).
3-118


